What is Environmental Chamber
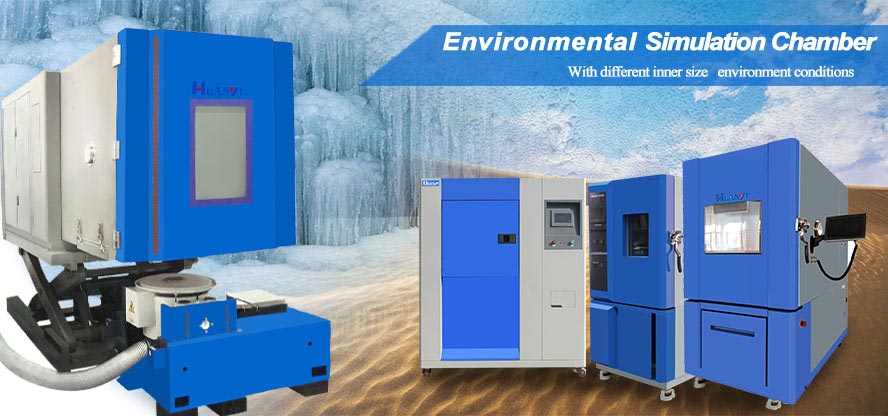
Environmental Chamber (Environmental Chamber), also called climate chamber in China, refers to a man-made design and construction that can simulate the real indoor space environment, and can control its temperature, humidity, airflow speed, air exchange frequency and other environmental factors through relevant technical means, and has a certain Volume test equipment.
According to the size, it can be divided into full-size environmental chamber (the space equivalent to the actual environment in which people live), medium-size environmental chamber and small-size environmental chamber. The main body of the current environmental warehouse is basically a rectangular parallelepiped made of stainless steel. The main structure includes an air purification system, a temperature control system, a humidity control system, and an airflow mixing device. The main parameters are volume, temperature, humidity, surface gas flow rate, and air exchange rate.
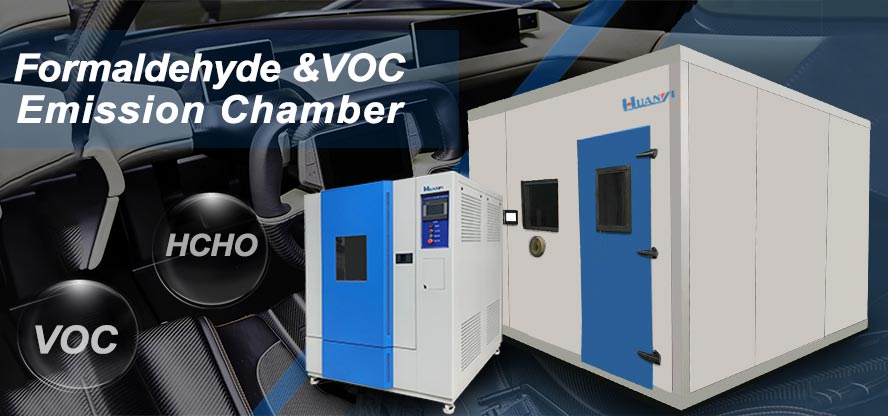
The main applications of environmental cabins include: routine evaluation of the hygienic quality of building decoration materials; research and investigation of the impact of environmental factors on the pollution release rate; research and investigation of the synergistic relationship between variables in various environments. At present, the main practical application is the evaluation of the hygienic quality of building decoration materials, that is, the detection of the release amount and release time of formaldehyde and VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds). Environmental cabins can be divided into small cabins and large cabins according to the size of the cabin. Small cabins generally refer to a volume less than or equal to 1m. The environmental cabin l2J is low in price and can be operated in several cabins at the same time. Only a few samples are needed. It is suitable for large-scale batch measurement of small samples and has good parallelism. Large cabins generally refer to large cabins with a volume greater than 10m, which are mainly used for large The measurement of parts and whole samples can simulate the real environment more accurately, but it requires expensive peripheral costs and operating costs.